LLAMADO and CERO
CONGRATS PHYSIO 1 HOTSHOTS
LLAMADO AND MONTINOLA

##############################################################################

CELLULAR RESPIRATION TUTORIAL
click and learn
click and learn II
click and learn III
########################################
 WHAT ARE GENES
WHAT ARE GENES
genes are made up of DNA. DNA in turn is made of mulititude of nucleutides. Nucleotide is a chemical compound made up of a nitrogen base, phosphoric acid and sugar.
genes are more known for its function in heredity but it is also respsonsible for the daily activity of the cell : that's why it is called the control center of the cell. Cytoplasmic activity is the due to enzyme-regulated chemical reactions. Genes dictate the kind of structural and globular protein that will be produced. The specialization of cellular function for instance is controlled by the genes.
But genes are inside the nucleus and to command cytoplasmic acitivity it needs to exert its control in the cytoplasm by some mechanism. This is thru RNA synthesis. With specificity of nitrogen base pairing this control mechanism of the genes is almost perfect till the code is translated in the cytoplasm
http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranslation.html
simplified transcription http://www.ncc.gmu.edu/dna/mRNAanim.htm
http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/molgenetics/transcription.swf
translation of the message simplified http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/molgenetics/translation.swf
what happened in mutationhttp://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Streisinger%20Model%20of%20Mutation.htm
when mutation occurs then that's the start of the malignant growth or cancer
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/cancer/grow_flash.html
######################################################
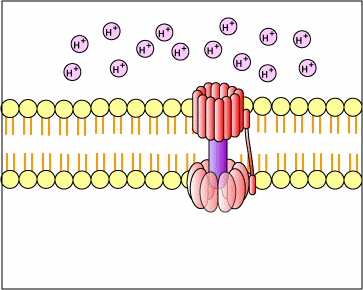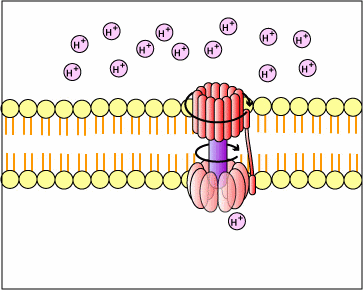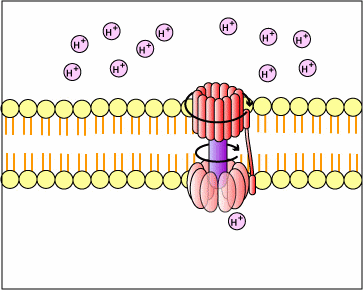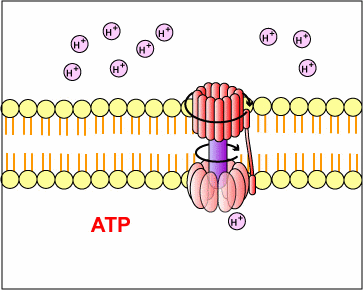
How Cells Make ATP
by PHOSPHORYLATION... adding a phosphate to ADP ADP + P ------> ATP
a) substrate level phosphorylation...
where a substrate molecule ( X-p ) donates its P to ADP making ATP b) chemiosmosis - [Oxidative Phosphorylation of Krebs cycle & ETC]... food substrates donate e- & protons to acceptor molecules [NADH], i.e., oxidation. NADH gives up electrons & protons are pumped out of mitochondria (or the chloroplasts in photosynthesis); protons diffuse back into mito thru an enzyme - ATPase, the ATPase enzyme makes ADP + P --> ATP figure * c) photophosphorylation.... e- of light energy, instead of food covalent bonds, are captured by chlorophylls to make a proton gradient across the chloroplast membranes... figure* protons move through a chloroplast ATPase enzyme to make ATP
http://student.ccbcmd.edu/biotutorials/energy/chemios.html
Oxidative Metabolism... (cell respiration) occurs in heterotrophic organisms that consume foods ... we say organisms oxidize (consume) foods (often glucose) to make energy because they remove & capture electrons... ... where is energy in foods? it's in the covalent bonds (e-)
Thus - METABOLISM is cells capturing e- via REDOX reactions REDOX REACTION... e- passed from one molecule to another [PGAL --> NAD+] in a chemical rx energy is transferred into the new molecule (a reeox couple) by holding e- OXIDATION = removal of electron &/or proton from food covalent bond REDUCTION = gaining electron &/or proton; adds an electron to an acceptor molecule
Cell RESPIRATION...
a more complete definition of cell respiration : - series of enzyme rx's (biochemical pathways) in the cytoplasm & mitochondria that, - remove e- (oxidation) from covalent bonds of substrates (as glucose), and - pass e- to acceptor molecules [coenzymes] such as NAD+ & FAD* which become reduced [ NADH & FADH2 ] - the reduced coenzymes [ NADH & FADH2 ] pass e- to other acceptors... a series of protein electron carriers called cytochromes, - the electron carriers [cytochromes] pass e- to O2 --reduction--> H2O - cytochromes also pump protons [H+] out of mitochondria into peri-mito space, - protons move back into mito thru a special enzyme (ATPase) & make ATP
KEY Reactions of KREBS CYCLE 1. NAD is reduced (NADH) and FAD is reduced (FADH2) 2. substrate level phosphorylation occurs (GTP <--> ATP) 3. decarboxylation [-COOH] 4.* an acylation reaction via coenzyme-A (forms Acetyl-coA) SUMMARY Reactions: [Krebs Cycle Quicktime Movie*] Summary figure full cycle*
######################################################################
CELLULAR TRANSPORT TUTORIAL
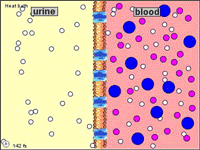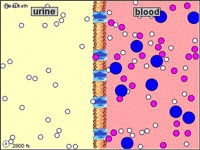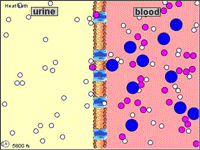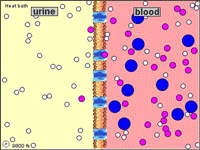
http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/membrane_transport/membrane_transport.htm
http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/membrane_transport/membrane_transport.htm
#########################################################################
MEMBRANE POTENTIAL TUTORIAL
check out this tutorial
sequence of events here
######################################################################
STUDY THIS PICTURE SHOWING THE DIFFERENT FLUID COMPARTMENTS
###############################################################
WHAT IS CRENATION
click here to learn
review the principles here
learn osmosis here
see how to doclotting time and bleeding time here
##############################################################
PLAY BLOOD TYPING
try your knowledge on blood typing and know what type of blood be transfused to different patient with different blood types
have fun and learn
http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/landsteiner/landsteiner.html
BLOOD TRANSFUSION REACTION
watch the animation here
http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation__cytotoxic__type_ii_hypersensitivity_.html
#####################################################################
HOW THE KIDNEY WORKS
nice animation how the kidney does its work
how kidney works
RENAL FUNCTION VIDEOlearn renal function here
FUNCTION OF NEPHRON TUTORIAL
review nephron's function here
RENIN ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM TUTORIAL
click here to know how this system corrects blood pressure
##############################################################
USEFUL LINKS FOR MUSCLE TWITCH ACTIVITY
pithing procedure
http://www.biopac.com/curriculum/pdf/a01.pdf
http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/neuro/muscle.htm
dissection for muscle nerve preparation
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QbxN63V-w7w&feature=related
ANTI-PITHING CAMPAIGN
http://www.frogsite.org/Anti_Pithing.html
MUSCLE TWITCH EXPERIMENT
understand the activity here
#######################################################
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
click and learn
BODY TEMPERATURE REGULATION
temperature regulation tutorial- click here
NEW!!!thermoregulationclick me
click me and learn
what is brown fat read here
#########################################################
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
gastric secretionclick me
FAT ABSORPTION
watch it here
more fatty help get greasy here
PROTEIN ABSORPTION watch it here
CARBOHYDRATE ABSORPTION right here
March 2, 2015 review the tutorial links of cellular respiration,body temperature regulation and GI system for the midterm. Take the practice quiz too...bet you it helps!
##################################################
##############################################
FEB. FRIDAY THE 13th 2015
INCENTIVE SPIROMETRY
How it is done
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LDgvhZjz0g8&feature=related
Deep breathing helps alveoli, the small air sacs deep in your lungs, fully expand. When you lie in bed for a long time (while recovering from injuries or surgeries, for instance) you tend to take shallow breaths and not cough as often as needed. You might start taking shallow breaths in an attempt to decrease pain associated with chest surgery or abdominal surgery.
Using an incentive spirometer will help you return to normal breathing rhythms. By inhaling deeply, you also help mobilize secretions and open areas of the lungs that my have collapsed.Using an incentive spirometer will mimic natural sighing and yawning and encourage you to take slow, deep breaths. Not only will this help restore your regular breathing rhythm, but it will also help you avoid atlectasis (a collapsed or airless condition of the lung) and pneumonia.
more reading check this out
##########################################################################
your prelims are disappointing..
study the links above re- cellular respiration and body temp regulations
Menstrual cycle tutorial
follow these links
monthly cycle click here for video tutorial
http://health.howstuffworks.com/menstruation.htm
HORMONAL CONTROL OF MENSTRUATION right here
http://msnbcmedia.msn.com/i/msnbc/Components/Interactives/Health/WomensHealth/zFlashAssets/menstrual_cycle_dw2%5B1%5D.swf
spermatogenesis and oogenesis spermatogenesis click here
NOTES ON SPERMATOGENESISright here
development and maturation of ovum
oogenesis
NOVEMBER 6
no more time for lecture...you are all expected to self-study the uncovered topics: male and female reproductive system , parturition..all these with GI system will be included in the finals...good luck guys
genes are more known for its function in heredity but it is also respsonsible for the daily activity of the cell : that's why it is called the control center of the cell. Cytoplasmic activity is the due to enzyme-regulated chemical reactions. Genes dictate the kind of structural and globular protein that will be produced. The specialization of cellular function for instance is controlled by the genes.
But genes are inside the nucleus and to command cytoplasmic acitivity it needs to exert its control in the cytoplasm by some mechanism. This is thru RNA synthesis. With specificity of nitrogen base pairing this control mechanism of the genes is almost perfect till the code is translated in the cytoplasm
http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranslation.html
simplified transcription http://www.ncc.gmu.edu/dna/mRNAanim.htm
http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/molgenetics/transcription.swf
translation of the message simplified http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/molgenetics/translation.swf
what happened in mutationhttp://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Streisinger%20Model%20of%20Mutation.htm
when mutation occurs then that's the start of the malignant growth or cancer
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/cancer/grow_flash.html
######################################################

How Cells Make ATP
by PHOSPHORYLATION... adding a phosphate to ADP ADP + P ------> ATP
a) substrate level phosphorylation...
where a substrate molecule ( X-p ) donates its P to ADP making ATP b) chemiosmosis - [Oxidative Phosphorylation of Krebs cycle & ETC]... food substrates donate e- & protons to acceptor molecules [NADH], i.e., oxidation. NADH gives up electrons & protons are pumped out of mitochondria (or the chloroplasts in photosynthesis); protons diffuse back into mito thru an enzyme - ATPase, the ATPase enzyme makes ADP + P --> ATP figure * c) photophosphorylation.... e- of light energy, instead of food covalent bonds, are captured by chlorophylls to make a proton gradient across the chloroplast membranes... figure* protons move through a chloroplast ATPase enzyme to make ATP
http://student.ccbcmd.edu/biotutorials/energy/chemios.html
Oxidative Metabolism... (cell respiration) occurs in heterotrophic organisms that consume foods ... we say organisms oxidize (consume) foods (often glucose) to make energy because they remove & capture electrons... ... where is energy in foods? it's in the covalent bonds (e-)
Thus - METABOLISM is cells capturing e- via REDOX reactions REDOX REACTION... e- passed from one molecule to another [PGAL --> NAD+] in a chemical rx energy is transferred into the new molecule (a reeox couple) by holding e- OXIDATION = removal of electron &/or proton from food covalent bond REDUCTION = gaining electron &/or proton; adds an electron to an acceptor molecule
Cell RESPIRATION...
a more complete definition of cell respiration : - series of enzyme rx's (biochemical pathways) in the cytoplasm & mitochondria that, - remove e- (oxidation) from covalent bonds of substrates (as glucose), and - pass e- to acceptor molecules [coenzymes] such as NAD+ & FAD* which become reduced [ NADH & FADH2 ] - the reduced coenzymes [ NADH & FADH2 ] pass e- to other acceptors... a series of protein electron carriers called cytochromes, - the electron carriers [cytochromes] pass e- to O2 --reduction--> H2O - cytochromes also pump protons [H+] out of mitochondria into peri-mito space, - protons move back into mito thru a special enzyme (ATPase) & make ATP
KEY Reactions of KREBS CYCLE 1. NAD is reduced (NADH) and FAD is reduced (FADH2) 2. substrate level phosphorylation occurs (GTP <--> ATP) 3. decarboxylation [-COOH] 4.* an acylation reaction via coenzyme-A (forms Acetyl-coA) SUMMARY Reactions: [Krebs Cycle Quicktime Movie*] Summary figure full cycle*
######################################################################
CELLULAR TRANSPORT TUTORIAL

http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/membrane_transport/membrane_transport.htm
http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/membrane_transport/membrane_transport.htm
#########################################################################
MEMBRANE POTENTIAL TUTORIAL
check out this tutorial
sequence of events here
######################################################################
STUDY THIS PICTURE SHOWING THE DIFFERENT FLUID COMPARTMENTS

Microcirculation is the delivery of fresh blood to the smallest blood vessels, present in the vasculature embedded within organ tissues.Arterioles carry the blood to the capillaries. Blood flows out of the capillaries into the venules. Arterioles contract and relax, varying their diameter and vascular tone, as the vascular smooth muscle responds to diverse stimuli.The term capillary exchange refers to all exchanges at microcirculatory level, most of which occurs in the capillaries. Sites where material exchange occurs between the blood and tissues are the capillaries. Capillary walls allow the free flow of almost every substance in plasma except plasma protein.Diffusion is the first and most important mechanism that allows the flow of small molecules across capillaries. The process depends on the difference of gradients between the interstitium and blood. The Starling equation is an equation that describes the roles of hydrostatic and osmotic forces (the so-called Starling forces) in the movement of fluid acrosscapillary endothelium.
########################################################################
MEMBRANE POTENTIAL --WHAT IS IT? membrane potential is but the negative electrical charge inside the cell brought about by the difference in ionic concentration in and out of the cell. This again is due to the selective permeability of the membrane to these ions
follow this link for tutorial of membrane and action potential
#####################################################################
find out how sodium potassium pump restore normal resting electrical gradient of the cell membrane after an action potential. Note the disparity in the number of ions it transport in and out of the cell. The net result is restoring the ionic and electrical gradient in the membrane.
http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/eustruct/sppump__rh_flash.html
###################################################################################################################
THE ACTION POTENTIAL TUTORIAL
check it out here
############################################################
 MUSCLE CONTRACTION TUTORIAL---http://www.brookscole.com/chemistry_d/templates/student_resources/shared_resources/animations/muscles/muscles.html
MUSCLE CONTRACTION TUTORIAL---http://www.brookscole.com/chemistry_d/templates/student_resources/shared_resources/animations/muscles/muscles.html
DO YOU KNOW WHAT IS EXCITATION CONTRACTION COUPLING check it out here
#########################
################################################
TUTORIAL ON TYPE OF TISSUES

this is a tutorial on different tissues and be able to take the self-evaluation test at the end of the tutorial...have fun and learn
http://www.zoology.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/tuthisto/intro.htm
click me
#########################################################
LECTURE SMOOTH MUSCLE CONTRACTION
check this out hereclick here
TUTORIAL ON SMOOTH MUSCLE
check this out
########################################################
USEFUL LINKS FOR MUSCLE TWITCH ACTIVITY
pithing procedure
http://www.biopac.com/curriculum/pdf/a01.pdf
http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/neuro/muscle.htm
dissection for muscle nerve preparation
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QbxN63V-w7w&feature=related
virtual lab : muscle twitch clcik here
ANTI-PITHING CAMPAIGN
http://www.frogsite.org/Anti_Pithing.html
MUSCLE TWITCH, SUMMATION AND MUSCLE TENSION
learn muscle twitch here
learn summation here
########################################################
ITS OCTOBER!
for lab activity please refer to the chapter: nervous regulation of blood pressure from Guyton
study the short term and long term regulation of blood pressure
###############################################################
BONE REMODELING
**remodeling here
**hormonal regulation of calcium here
mini lecture on cardiac cycle
click for some more fun
more lecture
click for cardiac cycle lecture 2
more tutorial on cardiac cycle
click here
cardiac cycle -click me
BARORECEPTOR
BARORECEPTOR ANIMATION
learn how does the baroreceptor works here
#########################################################
PHYSIO II
IMMUNE SYSTEM SWAT TEAM AT WORK watch video
watch it here
####################################################################
IMMUNE SYSTEM
check this out
humoral immune system explained
cell mediated immune system explained
beautiful simplified mechanism
mast cell and non-specific inflammatory response
HEMOSTASIS
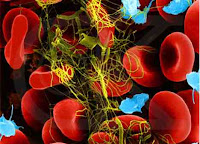 Its but rbc and platelets trapped in a meshwork of fibers called fibrin
Its but rbc and platelets trapped in a meshwork of fibers called fibrin
CLOTTING TEST TUTORIAL
click here how to do capillary test########################################################################
MEMBRANE POTENTIAL --WHAT IS IT? membrane potential is but the negative electrical charge inside the cell brought about by the difference in ionic concentration in and out of the cell. This again is due to the selective permeability of the membrane to these ions
#####################################################################
find out how sodium potassium pump restore normal resting electrical gradient of the cell membrane after an action potential. Note the disparity in the number of ions it transport in and out of the cell. The net result is restoring the ionic and electrical gradient in the membrane.
http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/eustruct/sppump__rh_flash.html
###################################################################################################################
THE ACTION POTENTIAL TUTORIAL
check it out here
############################################################
 MUSCLE CONTRACTION TUTORIAL---http://www.brookscole.com/chemistry_d/templates/student_resources/shared_resources/animations/muscles/muscles.html
MUSCLE CONTRACTION TUTORIAL---http://www.brookscole.com/chemistry_d/templates/student_resources/shared_resources/animations/muscles/muscles.htmlDO YOU KNOW WHAT IS EXCITATION CONTRACTION COUPLING check it out here
#########################
################################################
TUTORIAL ON TYPE OF TISSUES

this is a tutorial on different tissues and be able to take the self-evaluation test at the end of the tutorial...have fun and learn
http://www.zoology.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/tuthisto/intro.htm
click me
#########################################################
LECTURE SMOOTH MUSCLE CONTRACTION
check this out hereclick here
TUTORIAL ON SMOOTH MUSCLE
check this out
########################################################
USEFUL LINKS FOR MUSCLE TWITCH ACTIVITY
pithing procedure
http://www.biopac.com/curriculum/pdf/a01.pdf
http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/neuro/muscle.htm
dissection for muscle nerve preparation
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QbxN63V-w7w&feature=related
virtual lab : muscle twitch clcik here
ANTI-PITHING CAMPAIGN
http://www.frogsite.org/Anti_Pithing.html
MUSCLE TWITCH, SUMMATION AND MUSCLE TENSION
learn muscle twitch here
learn summation here
########################################################
ITS OCTOBER!
for lab activity please refer to the chapter: nervous regulation of blood pressure from Guyton
study the short term and long term regulation of blood pressure
###############################################################
BONE REMODELING
**remodeling here
**hormonal regulation of calcium here
mini lecture on cardiac cycle
click for some more fun
more lecture
click for cardiac cycle lecture 2
more tutorial on cardiac cycle
click here
cardiac cycle -click me
BARORECEPTOR
BARORECEPTOR ANIMATION
learn how does the baroreceptor works here
#########################################################
PHYSIO II
IMMUNE SYSTEM SWAT TEAM AT WORK watch video
watch it here
####################################################################
IMMUNE SYSTEM
check this out
humoral immune system explained
cell mediated immune system explained
beautiful simplified mechanism
mast cell and non-specific inflammatory response
Mast cells are present in most tissues in the vicinity of blood vessels, and are especially prominent near the boundaries between the outside world and the internal milieu, such as the skin, mucosa of the lungs and digestive tract, as well as in themouth and conjuntiva and nose
Mast cells play a key role in the inflammatory process. When activated, a mast cell rapidly releases its characteristic granules and various hormonal mediators into the interstitium and starts the inflammatory process
http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/inflammatory.html
Mast cells play a key role in the inflammatory process. When activated, a mast cell rapidly releases its characteristic granules and various hormonal mediators into the interstitium and starts the inflammatory process
http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/inflammatory.html
HEMOSTASIS
 Its but rbc and platelets trapped in a meshwork of fibers called fibrin
Its but rbc and platelets trapped in a meshwork of fibers called fibrin
These are the general processes involved in clot formation
1. vasoconstriction
2. formation of platelet plug
3. formation of clot
4. formation of fibrous tissue
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2002_general/Esp/folder_structure/tr/m1/s7/trm1s7_3.htm
1. vasoconstriction
2. formation of platelet plug
3. formation of clot
4. formation of fibrous tissue
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2002_general/Esp/folder_structure/tr/m1/s7/trm1s7_3.htm
CLOTTING TEST TUTORIAL
###############################################################
WHAT IS CRENATION
click here to learn
review the principles here
learn osmosis here
see how to do
##############################################################
PLAY BLOOD TYPING
try your knowledge on blood typing and know what type of blood be transfused to different patient with different blood types
have fun and learn
http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/landsteiner/landsteiner.html
BLOOD TRANSFUSION REACTION
watch the animation here
http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation__cytotoxic__type_ii_hypersensitivity_.html
#####################################################################
HOW THE KIDNEY WORKS
nice animation how the kidney does its work
how kidney works
RENAL FUNCTION VIDEOlearn renal function here
FUNCTION OF NEPHRON TUTORIAL
review nephron's function here
RENIN ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM TUTORIAL
click here to know how this system corrects blood pressure
##############################################################
USEFUL LINKS FOR MUSCLE TWITCH ACTIVITY
pithing procedure
http://www.biopac.com/curriculum/pdf/a01.pdf
http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/neuro/muscle.htm
dissection for muscle nerve preparation
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QbxN63V-w7w&feature=related
ANTI-PITHING CAMPAIGN
http://www.frogsite.org/Anti_Pithing.html
MUSCLE TWITCH EXPERIMENT
understand the activity here
#######################################################
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
click and learn
BODY TEMPERATURE REGULATION
temperature regulation tutorial- click here
NEW!!!thermoregulationclick me
click me and learn
what is brown fat read here
#########################################################
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
gastric secretionclick me
FAT ABSORPTION
watch it here
more fatty help get greasy here
PROTEIN ABSORPTION watch it here
CARBOHYDRATE ABSORPTION right here
March 2, 2015 review the tutorial links of cellular respiration,body temperature regulation and GI system for the midterm. Take the practice quiz too...bet you it helps!
##################################################
##############################################
FEB. FRIDAY THE 13th 2015
INCENTIVE SPIROMETRY
How it is done
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LDgvhZjz0g8&feature=related
Deep breathing helps alveoli, the small air sacs deep in your lungs, fully expand. When you lie in bed for a long time (while recovering from injuries or surgeries, for instance) you tend to take shallow breaths and not cough as often as needed. You might start taking shallow breaths in an attempt to decrease pain associated with chest surgery or abdominal surgery.
Using an incentive spirometer will help you return to normal breathing rhythms. By inhaling deeply, you also help mobilize secretions and open areas of the lungs that my have collapsed.Using an incentive spirometer will mimic natural sighing and yawning and encourage you to take slow, deep breaths. Not only will this help restore your regular breathing rhythm, but it will also help you avoid atlectasis (a collapsed or airless condition of the lung) and pneumonia.
more reading check this out
##########################################################################
your prelims are disappointing..
study the links above re- cellular respiration and body temp regulations
Menstrual cycle tutorial


follow these links
monthly cycle click here for video tutorial
http://health.howstuffworks.com/menstruation.htm
HORMONAL CONTROL OF MENSTRUATION right here
http://msnbcmedia.msn.com/i/msnbc/Components/Interactives/Health/WomensHealth/zFlashAssets/menstrual_cycle_dw2%5B1%5D.swf
spermatogenesis and oogenesis spermatogenesis click here
NOTES ON SPERMATOGENESISright here
development and maturation of ovum
oogenesis
NOVEMBER 6
no more time for lecture...you are all expected to self-study the uncovered topics: male and female reproductive system , parturition..all these with GI system will be included in the finals...good luck guys














