Thursday, December 5, 2013
Friday, November 29, 2013
Thursday, November 28, 2013
blood clot formation
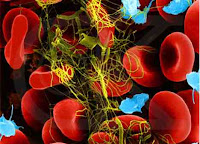
Its but rbc and platelets trapped in a meshwork of fibers called fibrin
These are the general processes involved in clot formation
1. vasoconstriction
2. formation of platelet plug
3. formation of clot
4. formation of fibrous tissue
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2002_general/Esp/folder_structure/tr/m1/s7/trm1s7_3.htm
check lecture slides on Jan.08 posting
1. vasoconstriction
2. formation of platelet plug
3. formation of clot
4. formation of fibrous tissue
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2002_general/Esp/folder_structure/tr/m1/s7/trm1s7_3.htm
check lecture slides on Jan.08 posting
PLAY BLOOD TYPING
try your knowledge on blood typing and know what type of blood be transfused to different patient with different blood types
have fun and learn
http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/landsteiner/landsteiner.html
have fun and learn
http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/landsteiner/landsteiner.html
Wednesday, November 20, 2013
Sunday, November 10, 2013
microscopic pictures of bacteria
see the bacilli here
http://www.mc.maricopa.edu/~johnson/labtools/Dbacyst/bacilli.html
see the cocci here
http://www.mc.maricopa.edu/~johnson/labtools/Dbacyst/cocci.html
and the rest here
http://www.mc.maricopa.edu/~johnson/labtools/Dbacyst/bacyst.html
http://www.mc.maricopa.edu/~johnson/labtools/Dbacyst/bacilli.html
see the cocci here
http://www.mc.maricopa.edu/~johnson/labtools/Dbacyst/cocci.html
and the rest here
http://www.mc.maricopa.edu/~johnson/labtools/Dbacyst/bacyst.html
Friday, November 8, 2013
Monday, November 4, 2013
spontaneous generation of life
Monday, September 30, 2013
Saturday, September 14, 2013
Tuesday, September 3, 2013
Monday, August 19, 2013
Saturday, August 10, 2013
muscle twitch
To understand the experiment on muscle twitch one should review the structure of skeletal muscle. How the muscle is able to contract minimally and maximally. This has something or everything to do with the so called motor units.
take a look at this animation to understand how summation of forces can increase force of contraction
Thursday, July 4, 2013
Wednesday, July 3, 2013
Monday, June 24, 2013
tutorial on types of tissue

this is a tutorial on different tissues and be able to take the self-evaluation test at the end of the tutorial...have fun and learn
http://www.zoology.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/tuthisto/intro.htm
click me
histology tutorial
learn the different types of tissue thru this tutorial link
take the histology practical exam - if you can do it here you'll do it in our practical exam
http://www.okc.cc.ok.us/deanderson/dennis-tutorial/histologydef.html
http://www.gwc.maricopa.edu/class/bio201/histoprc/prac1q.htm
take the histology practical exam - if you can do it here you'll do it in our practical exam
http://www.okc.cc.ok.us/deanderson/dennis-tutorial/histologydef.html
http://www.gwc.maricopa.edu/class/bio201/histoprc/prac1q.htm
Sunday, June 23, 2013
where did ATP come from? find out
How Cells Make ATP
by PHOSPHORYLATION... adding a phosphate to ADP ADP + P ------> ATP
a) substrate level phosphorylation...
where a substrate molecule ( X-p ) donates its P to ADP making ATP b) chemiosmosis - [Oxidative Phosphorylation of Krebs cycle & ETC]... food substrates donate e- & protons to acceptor molecules [NADH], i.e., oxidation. NADH gives up electrons & protons are pumped out of mitochondria (or the chloroplasts in photosynthesis); protons diffuse back into mito thru an enzyme - ATPase, the ATPase enzyme makes ADP + P --> ATP figure * c) photophosphorylation.... e- of light energy, instead of food covalent bonds, are captured by chlorophylls to make a proton gradient across the chloroplast membranes... figure* protons move through a chloroplast ATPase enzyme to make ATP
http://student.ccbcmd.edu/biotutorials/energy/chemios.html
Oxidative Metabolism... (cell respiration) occurs in heterotrophic organisms that consume foods ... we say organisms oxidize (consume) foods (often glucose) to make energy because they remove & capture electrons... ... where is energy in foods? it's in the covalent bonds (e-)
Thus - METABOLISM is cells capturing e- via REDOX reactions REDOX REACTION... e- passed from one molecule to another [PGAL --> NAD+] in a chemical rx energy is transferred into the new molecule (a reeox couple) by holding e- OXIDATION = removal of electron &/or proton from food covalent bond REDUCTION = gaining electron &/or proton; adds an electron to an acceptor molecule
Cell RESPIRATION...
a more complete definition of cell respiration : - series of enzyme rx's (biochemical pathways) in the cytoplasm & mitochondria that, - remove e- (oxidation) from covalent bonds of substrates (as glucose), and - pass e- to acceptor molecules [coenzymes] such as NAD+ & FAD* which become reduced [ NADH & FADH2 ] - the reduced coenzymes [ NADH & FADH2 ] pass e- to other acceptors... a series of protein electron carriers called cytochromes, - the electron carriers [cytochromes] pass e- to O2 --reduction--> H2O - cytochromes also pump protons [H+] out of mitochondria into peri-mito space, - protons move back into mito thru a special enzyme (ATPase) & make ATP
KEY Reactions of KREBS CYCLE 1. NAD is reduced (NADH) and FAD is reduced (FADH2) 2. substrate level phosphorylation occurs (GTP <--> ATP) 3. decarboxylation [-COOH] 4.* an acylation reaction via coenzyme-A (forms Acetyl-coA) SUMMARY Reactions: [Krebs Cycle Quicktime Movie*] Summary figure full cycle*
cellular transport tutorial
http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/membrane_transport/membrane_transport.htm
http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/membrane_transport/membrane_transport.htm
Friday, June 21, 2013
study this picture showing fluid compartments fo the body
.
Microcirculation is the delivery of fresh blood to
the smallest blood vessels, present in the vasculature embedded within organ
tissues.Arterioles carry the blood to the capillaries. Blood flows out of the
capillaries into the venules. Arterioles contract and relax, varying their
diameter and vascular tone, as the vascular smooth muscle responds to diverse
stimuli.The term capillary exchange refers to all exchanges at microcirculatory
level, most of which occurs in the capillaries. Sites where material exchange
occurs between the blood and tissues are the capillaries. Capillary walls allow
the free flow of almost every substance in plasma except plasma
protein.Diffusion is the first and most important mechanism that allows the
flow of small molecules across capillaries. The process depends on the
difference of gradients between the interstitium and blood. The Starling equation is an
equation that describes the roles of hydrostatic and osmotic forces (the so-called Starling forces)
in the movement of fluid acrosscapillary endothelium.
Thursday, May 16, 2013
DR. JUAN MIGUEL MURILLO Dean PT SPU
Saturday, April 20, 2013
attention micro special class
study both gm+ and gm- organisms.. diseases,signs, symptoms
antibiotics...classification..mechanisms of action
viruses...common diseases
fluid and hemodynamic derangement
neoplasm
antibiotics...classification..mechanisms of action
viruses...common diseases
fluid and hemodynamic derangement
neoplasm
Monday, April 1, 2013
SPU PT GRADS LIVING THEIR DREAMS
Dranreb Espura 2001, Las Vegas Nevada
Vanessa Espura 2002, Chicago, Illinois
Geordan Eula 2003,Taunton, Somerset
 onalyn Paguntalan-Barbecho.2003 Eugene, Oregon
onalyn Paguntalan-Barbecho.2003 Eugene, Oregon
 Carmela Ann Gilpo
Carmela Ann Gilpo
2006 New York City
 April Jane Corros
April Jane Corros
2002Gig Harbor, Washington
 Joanna cadiz,2004, new york
Joanna cadiz,2004, new york
 Francis Raymund Jarangue 2000, Federal way Washington
Francis Raymund Jarangue 2000, Federal way Washington
 Cherry Diaz-Estilo 2000, Waynesville, Wisconsin
Cherry Diaz-Estilo 2000, Waynesville, Wisconsin
 Tanya Jardeleza
Tanya Jardeleza
 Gazella Vagilidad-Abdallah, 2005, New York
Gazella Vagilidad-Abdallah, 2005, New York
 Aileen Sandoval, 2000 wa
Aileen Sandoval, 2000 wa
 Margaret Aguil Antiquiera. 2005 Mt. Vernon Wa
Margaret Aguil Antiquiera. 2005 Mt. Vernon Wa
 Diana Barrios, 2003, New York
Diana Barrios, 2003, New York
 ria Geinah Labanero. 2004. Mt. Vernon, WA
ria Geinah Labanero. 2004. Mt. Vernon, WA
 Karla Co, 2005, Florida
Karla Co, 2005, Florida
 Mary Joy Rivero, 2000, PA
Mary Joy Rivero, 2000, PA
 Anjanette Ang, 2000, Seattle, WA
Anjanette Ang, 2000, Seattle, WA
 Paul Raymund Evidente, 2001, PA
Paul Raymund Evidente, 2001, PA
 Mary Catherine Anas, 2000, California
Mary Catherine Anas, 2000, California
 Glenn aricaya,2002,Seattle ,WA.
Glenn aricaya,2002,Seattle ,WA.
 John Caesar Tapiculin,2000,New York & Filamae Garnica, 2000, Florida
John Caesar Tapiculin,2000,New York & Filamae Garnica, 2000, Florida
 Mark Jamantoc, 2002, Seattle WA
Mark Jamantoc, 2002, Seattle WA
Stephanie Jo Depositar,Carilion Stonewall Hosp
Lexington, Virginia
Vanessa Espura 2002, Chicago, Illinois
Geordan Eula 2003,Taunton, Somerset
 onalyn Paguntalan-Barbecho.2003 Eugene, Oregon
onalyn Paguntalan-Barbecho.2003 Eugene, Oregon Carmela Ann Gilpo
Carmela Ann Gilpo2006 New York City
 April Jane Corros
April Jane Corros2002Gig Harbor, Washington
 Joanna cadiz,2004, new york
Joanna cadiz,2004, new york Francis Raymund Jarangue 2000, Federal way Washington
Francis Raymund Jarangue 2000, Federal way Washington Cherry Diaz-Estilo 2000, Waynesville, Wisconsin
Cherry Diaz-Estilo 2000, Waynesville, Wisconsin Tanya Jardeleza
Tanya Jardeleza Gazella Vagilidad-Abdallah, 2005, New York
Gazella Vagilidad-Abdallah, 2005, New York Aileen Sandoval, 2000 wa
Aileen Sandoval, 2000 wa  Margaret Aguil Antiquiera. 2005 Mt. Vernon Wa
Margaret Aguil Antiquiera. 2005 Mt. Vernon Wa Diana Barrios, 2003, New York
Diana Barrios, 2003, New York  ria Geinah Labanero. 2004. Mt. Vernon, WA
ria Geinah Labanero. 2004. Mt. Vernon, WA Karla Co, 2005, Florida
Karla Co, 2005, Florida Mary Joy Rivero, 2000, PA
Mary Joy Rivero, 2000, PA Anjanette Ang, 2000, Seattle, WA
Anjanette Ang, 2000, Seattle, WA Paul Raymund Evidente, 2001, PA
Paul Raymund Evidente, 2001, PA Mary Catherine Anas, 2000, California
Mary Catherine Anas, 2000, California Glenn aricaya,2002,Seattle ,WA.
Glenn aricaya,2002,Seattle ,WA. John Caesar Tapiculin,2000,New York & Filamae Garnica, 2000, Florida
John Caesar Tapiculin,2000,New York & Filamae Garnica, 2000, Florida Mark Jamantoc, 2002, Seattle WA
Mark Jamantoc, 2002, Seattle WAStephanie Jo Depositar,Carilion Stonewall Hosp
Lexington, Virginia
Monday, March 25, 2013
membrane potential- what is it?
membrane potential is but the negative electrical charge inside the cell brought about by the difference in ionic concentration in and out of the cell. This again is due to the selective permeability of the membrane to these ions.
http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp44/4401s.swf
http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp44/4401s.swf
Sunday, March 24, 2013
principle of diffusion
How molecules distribute itself in microcirculation. Transfer of substances in three compartments: intracellualry and extracellularly( interstitial and intravascularly).
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_diffusion_works.html
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_osmosis_works.html
what creates the pressure? It is kinetic motion of of particles that exert the pressure as it collide against each other in a give compartment. Watch and answere some questions
http://www.chm.davidson.edu/ChemistryApplets/KineticMolecularTheory/Pressure.html
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_diffusion_works.html
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_osmosis_works.html
what creates the pressure? It is kinetic motion of of particles that exert the pressure as it collide against each other in a give compartment. Watch and answere some questions
http://www.chm.davidson.edu/ChemistryApplets/KineticMolecularTheory/Pressure.html
sodium pump - an electrogenic pump
find out how sodium potassium pump restore normal resting electrical gradient of the cell membrane after an action potential. Note the disparity in the number of ions it transport in and out of the cell. The net result is restoring the ionic and electrical gradient in the membrane.
http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/eustruct/sppump__rh_flash.html
http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/eustruct/sppump__rh_flash.html
Saturday, March 23, 2013
micro 2013 topnotch
lecture: FAMA,
Bordones, Wong, Caram, Acervo
lab : JUAREZ, SALVALEON
Estilo, Evidente, Tuminez
Bordones, Wong, Caram, Acervo
lab : JUAREZ, SALVALEON
Estilo, Evidente, Tuminez
Thursday, March 21, 2013
Wednesday, March 20, 2013
Tuesday, March 12, 2013
Thursday, February 21, 2013
Tuesday, February 5, 2013
identification of bacteria
try these exciting online methods of identification of bacteria, by staining and speciating it by pcr and more
enter the lab
bio-alive:bacterial identification
Monday, January 7, 2013
Thursday, January 3, 2013
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)




